Business Intelligence Tools That Improve Maintenance: A Modern Approach
In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficiency and strategic decision-making are paramount. For maintenance departments, this translates to optimized operations, reduced downtime, and ultimately, cost savings. This is where business intelligence tools that improve maintenance come into play. They provide the data-driven insights needed to transform reactive maintenance into proactive, predictive strategies. This article explores the powerful capabilities of these tools and how they are revolutionizing maintenance practices across various industries.
The Evolution of Maintenance: From Reactive to Predictive
Traditionally, maintenance was a reactive process. Equipment would break down, and then repairs would be initiated. This approach led to significant downtime, unexpected costs, and reduced productivity. The evolution of maintenance has seen a shift towards preventative and predictive strategies. These strategies leverage data to anticipate potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This shift requires sophisticated tools and a data-driven mindset.
Understanding Business Intelligence (BI) and Its Role in Maintenance
Business intelligence (BI) refers to the technologies, applications, and practices used to collect, integrate, analyze, and present business information. In the context of maintenance, BI tools gather data from various sources, including sensors, maintenance logs, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This data is then analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that can inform maintenance decisions. The key is to transform raw data into actionable insights.
Key Features of Business Intelligence Tools for Maintenance
Effective business intelligence tools that improve maintenance offer a range of features designed to optimize operations. These features are crucial for maximizing the value of maintenance data. They also provide the ability to make informed decisions.
- Data Collection and Integration: The ability to collect data from multiple sources, including IoT sensors, CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System), and other operational systems. This integration is essential for a holistic view.
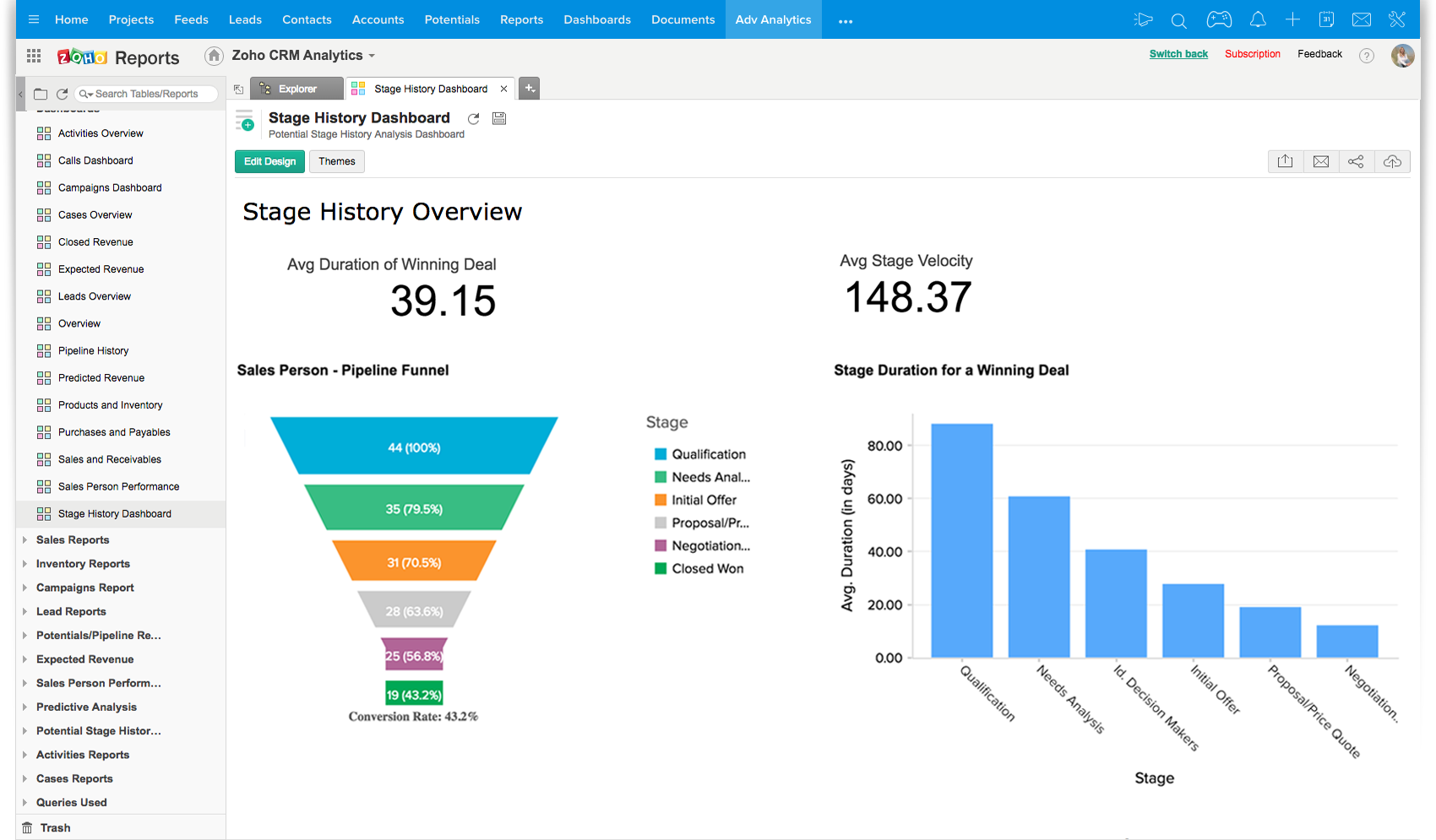
- Data Visualization: Interactive dashboards and reports that present complex data in an easily understandable format. Visualizations help identify issues quickly.
- Predictive Analytics: Algorithms that analyze historical data to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This minimizes downtime.
- Performance Monitoring: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that track maintenance efficiency, such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time To Repair (MTTR). These KPIs help measure success.
- Reporting and Alerting: Automated reports and alerts that notify maintenance teams of potential issues or performance deviations. This enables quick response.
Top Business Intelligence Tools for Maintenance
Several business intelligence tools that improve maintenance are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The best choice depends on the specific needs of the organization. Here are some of the most popular and effective tools:
Tableau
Tableau is a widely-used BI tool known for its user-friendly interface and powerful data visualization capabilities. It allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports quickly, making it ideal for presenting maintenance data in an accessible format. Tableau’s drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to create visualizations. It also simplifies data analysis. Tableau is a strong choice for organizations needing to quickly understand and communicate maintenance performance.
Power BI
Microsoft’s Power BI is another popular choice, especially for organizations already using other Microsoft products. Power BI offers a range of features, including data integration, data modeling, and advanced analytics. Its tight integration with Excel and other Microsoft applications makes it easy to adopt and use. Power BI’s competitive pricing makes it a cost-effective option. It is suitable for a wide range of maintenance applications.
IBM Cognos Analytics
IBM Cognos Analytics is a comprehensive BI platform designed for enterprise-level deployments. It offers advanced analytics capabilities, including predictive modeling and statistical analysis. Cognos provides robust reporting features and strong data governance capabilities. It is well-suited for large organizations with complex maintenance needs. Cognos excels in handling large datasets. It offers advanced analysis capabilities for detailed insights.
SAP Analytics Cloud
SAP Analytics Cloud is a cloud-based BI solution designed to integrate with SAP systems. It offers features for data visualization, predictive analytics, and planning. Its focus on integration with SAP makes it a good choice for organizations using SAP ERP systems. The cloud-based nature of SAP Analytics Cloud provides flexibility. It also offers easy access to maintenance data.
Other Notable Tools
Several other business intelligence tools that improve maintenance deserve mention. They may be specifically designed for maintenance or offer unique features:
- Seeq: A specialized tool for analyzing time-series data from industrial sensors.
- UpKeep: A CMMS with integrated BI features.
- eMaint: A cloud-based CMMS with BI reporting capabilities.
Benefits of Using Business Intelligence in Maintenance
Implementing business intelligence tools that improve maintenance provides numerous benefits. These benefits translate into improved operational efficiency and cost savings. They also lead to better decision-making.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance helps to identify potential failures before they occur, minimizing unplanned downtime. This increases productivity.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Optimized maintenance schedules and reduced equipment failures lead to lower labor costs and parts expenses. This improves the bottom line.
- Improved Asset Performance: By monitoring equipment performance and identifying areas for improvement, BI tools help to extend the lifespan of assets. This enhances the value of assets.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data-driven insights enable maintenance teams to make more informed decisions about resource allocation and maintenance strategies. This improves efficiency.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation and streamlined workflows improve the efficiency of maintenance operations. This saves time and resources.
Implementing Business Intelligence in Maintenance: A Step-by-Step Approach
Successfully implementing business intelligence tools that improve maintenance requires a strategic approach. A well-defined implementation plan ensures a smooth transition and maximizes the benefits.
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of implementing BI in maintenance. What specific problems are you trying to solve? This sets the direction.
- Assess Data Sources: Identify the data sources that will be used for analysis, including sensors, CMMS, and ERP systems. Understand the data available.
- Choose the Right Tool: Select the BI tool that best fits the organization’s needs and budget. Consider features, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
- Implement Data Integration: Establish data connections and integrate data from different sources into the BI platform. This is crucial for a holistic view.
- Develop Dashboards and Reports: Create interactive dashboards and reports that visualize key maintenance metrics. This provides insights.
- Train Users: Provide training to maintenance staff on how to use the BI tool and interpret the data. This ensures effective use.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of the BI system and make adjustments as needed. This ensures ongoing value.
Challenges and Considerations
While business intelligence tools that improve maintenance offer significant benefits, there are also challenges to consider. Addressing these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data is critical. Implement data validation and cleansing procedures. This ensures data integrity.
- Data Security: Protect sensitive maintenance data from unauthorized access. Implement appropriate security measures. This protects valuable information.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating data from multiple sources can be complex. Plan for data mapping and transformation. This streamlines the process.
- User Adoption: Training and user support are essential to ensure that maintenance staff embrace the new tools and processes. This ensures successful adoption.
- Cost: Implementing BI tools can involve significant costs, including software licenses, hardware, and training. Consider the budget.
The Future of Business Intelligence in Maintenance
The future of business intelligence tools that improve maintenance is bright. Technological advancements will continue to drive innovation in this area. These advancements will further optimize maintenance practices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning algorithms will enhance predictive maintenance capabilities. This will lead to even more accurate failure predictions.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The increasing use of IoT sensors will provide more real-time data for analysis. This will enable more proactive maintenance.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based BI solutions will become more prevalent, offering greater flexibility and scalability. This will improve accessibility.
- Mobile BI: Mobile dashboards and reports will enable maintenance teams to access data from anywhere. This will improve mobility.
Conclusion
Business intelligence tools that improve maintenance are transforming the way maintenance departments operate. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can optimize maintenance schedules, reduce downtime, and improve asset performance. Implementing these tools requires a strategic approach, but the benefits are substantial. As technology continues to evolve, BI will play an even greater role in shaping the future of maintenance. Companies that embrace these tools will gain a significant competitive advantage. They will also achieve greater operational efficiency. This will lead to increased profitability and sustainability. Embrace the power of data. Transform your maintenance practices. [See also: The Impact of Predictive Maintenance on Operational Efficiency] [See also: How to Choose the Right CMMS for Your Business] [See also: Leveraging Data Analytics for Enhanced Asset Management]